We work with msconfig. Learning to use Msconfig How to open msconfig
Good day, dear readers of my blog.
Each PC or laptop, in addition to user-installed software, also has built-in software. There are often situations when, for some reason, the client needs to configure the operation of the device. For this purpose, developers at Microsoft have provided a useful and convenient utility MSConfig Windows 7.
The program is a powerful tool that allows you to debug autorun in detail and remove some errors that interfere with the correct operation of the system.
The "" application has extensive capabilities in the segment of setting up a personal computer or laptop. For easy use, the developer has divided the working window into several key tabs.

Important! You should not disable/enable parameters if you are not sure of your actions.
This tool is designed for detailed system configuration. In most cases, this is done to speed up its work.
Tabs( )
As mentioned above, the window is divided into several segments:
On the "" tab, the user can choose which startup type to install for Windows 7.
» will help you configure the process of starting the system in more detail. So, for example, here you set the time needed to start. In addition, if necessary, you can immediately select “” if there is no other way to enter it. How to enable multiple processes? You need to click on " Extra options…» and select the appropriate menu. Some other settings are also set there.

Tab " Services"Allows a person to manage all existing system processes. Here you can stop or start them. At the same time, the tab provides a “” item, by clicking on which the user can see a shortened list of utilities installed by the person.

" is considered the most popular tab among clients used by Windows. Here you can view the number of processes that start when the operating system starts. There is an option to turn them off and on.

The “” tab contains tools for launching basic OS features, which will also help optimize the operation of your computer.

After you change something, you need to confirm your actions with the “ Ok" And for the changes to take effect, you need to reboot, which the system itself will notify immediately after closing. For convenience, the restart can be postponed.
Launching "System Configuration"( )
So, how do we access the tool we need? There are several different options to see the menu you want.
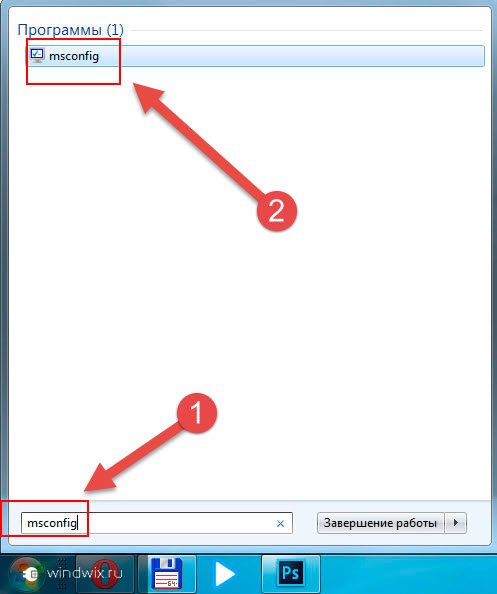
Let's go to " Start" and enter "" in the search bar. We wait for the results to appear and select the appropriate application. Usually it occurs alone. How to open the program? Just click on the icon with the left mouse button.
We also go to the menu “ Start", and then select " All programs" Let's go to the catalog " Service" And " Standard" We need " Command line».
A new window will open where you need to enter “” and then confirm by pressing “ Enter».

We go back to the same place Start"to the team" Execute" To do this, you can also press the combination “ Win+R».
A small window will appear where we enter “” and then confirm our actions.

It must be said right away that this method is the longest. Almost no one uses it. But in any case, you should know about it. So where is the right program? We need to open " Computer", system disk, go to " Windows", and then go to "". Here we are looking for the application “”. It launches with a simple double click of the mouse.

Sometimes one of the path nodes may be hidden and simply not visible. To restore you need to click " View», « Options» and on the second tab uncheck the necessary checkboxes at the end of the list.
The program doesn't work( )
Some users may encounter a situation where the required utility does not start. A message appears stating that the required file simply does not exist at the specified address.
In most cases, this happens as a result of a virus entering the computer, which simply deletes the application. What to do?
First, we check the system with a good antivirus with new databases. Otherwise, you simply don’t have to do the rest.
Next, we look to see if a suitable file exists in its usual place. If it is not there, we try to copy the element from the same operating system installed on another PC. It is also extracted from the disk where the OS image is located.
To do this, run “ Execute" by using " Win+R"or in any other way. In the window that opens, write the following:
Expand "image location"\i386\MSCONFIG.EX_C:\Windows\system32\msconfig.exe, and confirm our intentions. Wherein " image location"—the drive letter where the system files are located or the path to them (if located directly on the computer).
There is also an option to simply download “ msconfing.exe» from the Internet and place this file in a folder located along the path that I mentioned earlier.
Of course, a complete reinstallation of Windows is more effective and definitely effective. This will also speed up your computer overall. But not everyone can do this on their own or simply don’t want to.
Sometimes, for some reason, a required system component does not start due to restricted access rights. To check, we try to open the program with Administrator rights. This usually helps.
In addition, we try to launch the application in "". To do this, reboot and before the OS starts loading, press “ F8" Then select the appropriate item.

Next, it is advisable to check “ Registry Editor" To do this, go to “ Execute" and write " regedit" Next we go to “ HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE", folder " Software" Then we go to " Microsoft», « Windows», « CurrentVersion" And " AppPaths" We are interested in the msconfig file with the extension *.exe. Or rather, simply its presence. Additionally, the value of REG_SZ should be: C:\Windows\system32\msconfig.exe. If this line or even the corresponding mark does not exist, all this needs to be created.
In addition, there is a mechanism for checking operating system system files. To do this, go to “ Execute"(we already know how this can be done). In the window that opens, enter “ sfc /scannow" We confirm our intentions. Should open " Windows File Protection”, which will be accompanied by the message “ Checking in progress..." If the tool manages to determine that the files have changed, it will report this and offer to restore everything to the original version using the installation disk.
Settings( )
If the system component is working correctly or you have corrected possible errors, you can begin to use it directly. How to properly configure the operating system using this tool? It all depends on what components a particular user uses.
If we talk about what can be disabled in msconfig in general, you can find out from what I wrote earlier. In particular, it talks about the tab “ Services».
Moreover, if you disable all the components described above, and also clean the “” partition as much as possible,” you can even achieve maximum performance of your equipment. It is important to remember that any systemic changes usually lead to consequences. So, if you are not sure of the correctness of your actions, you should not change anything.
Well, it turns out that the MSConfig tool is a useful element of the system. If you use it correctly, you can significantly increase the speed of your device. In this case, incorrect handling can damage the system.
I hope this article helps you. Subscribe and tell your friends about my blog.
26.11.2009 22:52
System Setup- This diagnostic a tool designed to configure Windows 7 startup settings in order to identify the causes of problems with the computer and operating system. Using the System Configuration program, you can identify drivers, programs and components that, due to incorrect operation, cause errors during the startup and operation of Windows 7.
Launching the System Configuration Program
To launch System Setup, open the Start menu, type in the search bar, and press Enter.
You can also use the keyboard shortcut Windows + R, enter and press OK.

General tab

On the tab You can choose one of three options for starting the operating system:
Normal launch
In this mode, Windows 7 starts in the normal way. “Normal startup” is used when there are no problems loading the OS or after troubleshooting.
Diagnostic run
In diagnostic startup mode, only the basic services and drivers necessary for the functioning of the operating system and computer are launched along with Windows. If the problem does not disappear when diagnostic startup is enabled, then most likely the main Windows files and drivers are damaged. If there are no problems when diagnostic startup is enabled, then you need to use the mode Selective launch.
Selective launch
In this mode, Windows 7 starts using basic services and drivers, as well as other services and automatically loaded programs selected by the user. Three additional options are available:
- Load system services– if this parameter is enabled, then the operating system boots with a standard set of services necessary for its operation.
- – if this parameter is enabled, then programs marked with checkboxes on the tab are launched along with the operating system.
- – This option is enabled by default and is grayed out. This option restores the original Windows 7 startup settings if changes are made on the tab.
Selective startup should be used if diagnostic run passed without errors. Turn on additional services and programs one by one, and monitor the system until you identify the cause of the errors.
Loading tab

Default operating system
If you have multiple operating systems installed on your computer, you can designate any of them as the default boot one. To do this, highlight the desired operating system and click the button Use as default.
You can also set a custom multiboot menu delay time by setting the time in seconds in the field Time-out.
To remove an operating system from the list, select it and click the button Delete.
Safe mode
Safe mode is a mode of operation of the operating system with a limited set of services, devices and drivers necessary for the functioning of the computer.
Windows services that start in safe mode:
- Windows Event Log
- Plug and Play device support
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
- Cryptography Services
- Windows Defender
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Devices and drivers that run in safe mode:
- Internal hard drives (ATA, SATA, SCSI)
- External hard drives (USB)
- Floppy drives (internal and USB)
- Internal CD and DVD drives (ATA, SCSI)
- External USB drives for CDs and DVDs
- Keyboards and mice (USB, PS/2, serial port)
- VGA video cards (PCI, AGP)
Check the box Safe mode and select one of the download options:
Minimum– launch Windows 7 Explorer in safe mode using only basic Windows devices, drivers and services, without network support.
Another shell– loading the command line, basic devices, drivers and services of Windows 7. Explorer and network components are disabled.
Active Directory Recovery– launch Windows 7 Explorer in safe mode using only essential services, devices and drivers, as well as the Active Directory directory service.
Net– launch Windows 7 Explorer in safe mode using only the main components of the operating system, as well as the following network components:
- Network adapters (wired Ethernet and wireless 802.11x)
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP
- Network connections
- NetBIOS support module over TCP/IP
- Windows Firewall
Download log– all information about the Windows 7 boot process is saved to a file %SystemRoot%/Ntbtlog.txt.
Basic video– standard VGA drivers are loaded instead of drivers corresponding to the video card.
OS information– When Windows 7 boots, the names of the downloaded drivers are displayed.
Make these boot options permanent– if this option is enabled, then the system settings you have changed can only be canceled manually. You cannot undo changes by selecting Normal Startup on the General tab. Also you will not be able to undo changes using the function Use original boot configuration on the tab .

To configure advanced boot options for Windows 7, on the tab, click Extra options.
Number of processors
This setting allows you to limit the number of both real and virtual processors used in the system. Select the checkbox and use the drop-down list to specify the number of processors that you want to use starting from the next system startup.
Maximum memory capacity
This setting allows you to limit the amount of physical RAM used by the operating system. Select the checkbox and in the text field specify the maximum amount of RAM (in megabytes) that will be used by the system starting from the next startup.
PCI blocking
If this setting is enabled, the operating system does not allocate I/O and interrupt resources on the PCI bus. In this case, the I/O and memory resources specified in the BIOS are preserved.
Debugging
When enabled, you can set global kernel-mode debugging options for device driver developers.
Services Tab

Tab Services contains a list of services that start automatically when Windows 7 boots. All these services are divided into two categories:
- Microsoft services, on which the operation of the operating system depends;
- third party services, necessary for the operation of drivers and some programs.
When identifying the causes of problems that occur during startup or operation of Windows 7, you need to follow these steps:
1. On the tab
- Turn on Selective launch.
- Check the box Load system services.
- Uncheck Load startup items.
2. On the tab Services:
- Check the box .
- Disable all third party services from running.
3. Restart your computer.
If problems do not occur after a reboot, then the Windows 7 system components are working properly, and the cause of the errors is most likely the incorrect operation of one or more third-party services. To identify which service is causing the failure, enable one service at a time, restart the computer, and monitor the system status.
If your system still experiences errors after disabling third-party services, the underlying operating system components may be damaged. To identify the cause of the errors, follow these steps:
1. Uncheck Don't display Microsoft services.
2. Disable all Microsoft services, then enable them one at a time, restart your computer and monitor the changes until you identify all the services causing the failure.
Startup tab

- In column Startup item The program name is displayed.
- In column Manufacturer- program developer.
- In column Team the executable file that runs with the OS is indicated, as well as the location of this file.
- In column Location The registry key responsible for automatically starting the program along with Windows 7 is displayed.
- In column Shutdown date The date for disabling startup items that do not start automatically with the operating system is indicated.
If problems arise in Windows 7, you can try to determine the cause of the problem by disabling automatic program launch one by one. To identify which program is causing the crash, turn off the startup of all programs, and then turn on one program at a time, restart the computer and monitor the system status.
To prevent the program from starting with Windows 7, you need to uncheck the box next to its name and click the button Apply.
Service tab

Tab allows you to quickly launch Windows configuration, administration, and diagnostic tools. Select the desired tool and press the button Launch.
About the program– displays information about the version of Windows 7 installed on the computer.
Change User Account Control settings– setting up UAC, a Windows 7 security component that requests confirmation of actions that require administrator rights.
Support Center- The main place to view alerts and take actions that help Windows 7 run smoothly. Action Center lists important messages about security and computer maintenance settings that require your attention.
– a set of tools for automatically resolving some common problems when working with networks, hardware and devices associated with the use of the Internet, as well as program compatibility problems.
Computer management– a set of tools for managing hardware, software and network components of Windows 7.
System Information– a Windows 7 component that displays detailed information about your computer's hardware configuration, components, and software, including drivers.
Event Viewer– a tool for viewing detailed information about important events that occur in the system (for example, programs that do not start properly or updates that are downloaded automatically). This information may be helpful in troubleshooting problems and errors in Windows 7 and installed programs.
Programs– Windows 7 Programs and Features tool, designed to enable or disable Windows 7 components, as well as to remove programs or change their configuration.
Properties of the system– basic information about the hardware and operating system. Windows 7 version and activation status, performance index, computer name, domain name, and workgroup settings.
Internet Options– Internet Explorer browser settings.
IP protocol configuration– view and configure the computer’s network address (in the command line).
is a powerful diagnostic and performance monitoring tool built into Windows 7.
Resource Monitor– A tool for viewing processor, hard drive, network, and memory usage in real time.
Task Manager– displays applications, processes and services that are currently running on the computer. You can use it to monitor your computer's performance or stop applications that are not responding. Monitoring the network status and viewing its operating parameters.
Command line- A Windows 7 feature that allows you to enter MS-DOS and other commands without a graphical user interface.
Registry Editor– a tool designed to view and change settings in the system registry, which contains information about the operation of the computer.
When the need arises to configure the Windows operating system, many users resort to using a variety of utilities from third-party developers. At the same time, without even suspecting the existence of built-in tools for solving these problems.
One of the most powerful and simplest configuration tools is the msconfig utility. It can be run on any computer running the Windows operating system, and you do not need to install any additional programs. With this program you can manage the loading of the operating system, installed services and. In addition, using this program you can quickly launch other built-in tools for managing the operating system. In this article we will try to consider the msconfig program and its main capabilities in as much detail as possible.
Launching msconfig is very simple, and there are several ways to do it. The easiest way is to start using search. Open the Start menu or Start screen if you have Windows 8 and type "msconfig". After this, you just need to click on the program icon.

Launching a program using the Start menu
You can also use the Run menu. To launch the Run menu, press the Win + R key combination. After that, enter the command “msconfig” and press enter.

Running a program using the Run menu
In addition, msconfig can be run using the command line or from the folder, the msconfig.exe program can be found in the Windows\System32 folder.
Configuring Windows using msconfig
So, we have launched msconfig, we can get to work. The interface of this program consists of several tabs: General, Download, Services, Startup and Service. Let's look at all the tabs in order.

General Tab
On the General tab, you can select the operating system boot option.
- Normal startup – startup with loading of all drivers and services.
- Diagnostic startup - startup with loading only the main drivers and services.
- Selective launch – launch with loading of selected elements of the operating system.

The second tab is called "Download". Here you can configure the operating system boot process. For example, if you have multiple versions of Windows installed on your computer, you can specify which system will boot by default. Here you can also specify other settings related to loading the operating system.
The third and fourth tabs are the most useful for the average user. The third tab is called “Services”; here you can disable/enable services installed on the system.

Services Tab
If you do not have the proper experience, then it is better not to disable standard services. This may cause the operating system to become unstable. To hide standard services, check the box next to “Hide Microsoft services.”

Don't display Microsoft services
Moreover, after hiding standard services, working with the list becomes much easier. You can easily find and disable services that you do not need, which will increase the speed of the system.
The fourth tab is called “Startup”. Here you can manage programs that load automatically when the operating system starts. For example, you can.

The last tab in the msconfig utility is the Tools tab. Here you can launch other standard tools for managing the operating system.

Service tab
To do this, select the desired tool in the list and click on the start button.
How to use msconfig?
There can be many scenarios for using the msconfig program. In most cases, ordinary users use msconfig to remove unnecessary programs from startup and disable services.
Also, msconfig can be used as a tool for diagnosing and testing the system. You can run the operating system using diagnostic startup and check its stability. If the operating system continues to fail in this mode, then most likely the problem is in the system files. If the system works stably, then the problem is in the installed applications.
The article describes what the utility is msconfig, what are its main benefits and how to use it correctly to solve problems with Windows and prepare the way for error testing.
Among other repair utilities included in Windows, msconfig.exe(aka utility System Configurations) certainly stands apart. It is most often used for:
- configuration of the system startup type (selection of a special mode)
- changing the boot procedure
- selection of services and programs at system startup
- launching special repair or statistical utilities
The configuration utility is a window of several tabs, and in the latest version of Windows, one of them () has moved to the Task Manager. Msconfig.exe is launched in several ways, the simplest of which is:
WIN+R->msconfig
Let's check each of the tabs:
Msconfig: select services and drivers for Windows
The first tab will be Are common. Here we will be greeted by several points characterizing the option to start services and drivers.

- Normal launch– an option that occurs by default and is saved from the moment you install Windows. At this time, the system will load drivers for all installed (and subsequently installed) devices and those services that, according to Windows, are needed for operation, if the system does not register any errors in operation. There is no need to change anything in this option... as long as the user has not changed anything in the list of services, in the startup folder or other settings. As soon as you make changes to the startup method, prohibit programs from starting, change the task schedule, or add your own, the startup option automatically changes to Selective startup
- Diagnostic run– this option is somewhat reminiscent of Windows Safe Boot Mode. After a reboot, only the drivers and services of the system itself will work in it: no other programs or third-party drivers will start working, and previously installed and updated drivers will be replaced with those that “arrived” with the Windows installation (so to speak, international ones). However, antivirus software is often included in this privileged list. The meaning is clear - this launch option is used in an attempt to isolate the problematic part of the software when the OS is unstable
- Selective launch will allow you to boot the system, bypassing programs that have been prescribed over time, loading (or not loading) the main services. By setting or deleting the autoload setting, you can determine whether its contents are interfering with normal operation, or whether the reason lies elsewhere. A changed item with the original boot configuration means that you have made changes to the boot record. This often happens when using a multiboot system with 2 or more operating systems, when editing local disks (letters, size or deleting/recreating volumes), etc.
The next tab displays a list of Windows systems as the bootloader sees them. So, if you have a second Linux installed, the bootloader rightly has no idea about this. The same applies to Windows OS of different generations: when it was in fashion Windows XP, its bootloader about Windows 7 or 10 and never heard of it. So what about Windows 10 in the bootloader from Windows XP there is nothing. But 10 already knows everything about previous versions of the Microsoft OS, so they are great. But for security reasons, correction of the list of systems in this part of the window is excluded: you will not be able to rename, delete from here, or rearrange them, since the utility is not granted such rights. This option is presented for purely informational purposes.
However, the lower part of the tab window already contains customizable options, some of which may be useful. The simplest, but required - Time-out-change the display time of the menu for selecting operating systems (if there are several of them). By default, Windows leaves us 30 seconds for this. If there is only one system, the bootloader is wise to omit the menu. But if there are 2 or more copies of Windows, you don’t have to wait half a minute, but set the desired time.

On the left are special boot options. Among them is the notorious Safe Mode, which completely prevents the launch of programs and drivers other than those installed by the system. Moreover, in addition to the option itself, you can set additional parameters for Safe Mode, including:
– Safe mode with a full user interface, but disabled network driversThe functionality of the utility continues with the next column of settings, which will allow the user to change some boot parameters in both Safe Mode and Normal Mode. Something like this:
- Without GUI– during boot you will not see the usual welcome screen, only a black screen without any information
- Download log– after downloading, all information about running services and drivers is entered into a special log file, which can be found at C:\Windows\Ntbtlog.txt
- Basic video– a very useful parameter that allows you to load an image from a video card using ONLY drivers pre-installed by the system (and not those that you installed from the video disk, downloaded from the Internet, etc.). An important option when something goes wrong after updating your video driver
- OS information– the option must be used with the Without GUI. The system boot will be accompanied by a black screen displaying complete information on the loaded drivers. If the system crashes during boot, this mode can help identify the driver that causes the system to crash.
Button : options are not for everyone
The only available button in this quadrant of the window is Additional boot options, where you can force a given copy of Windows to start, either ignoring the data from or, on the contrary, strictly following it (this part of the tab was left by the developers at the beta stage: they pushed through some settings for testing, but they were “forgotten there”).

For example, you can ask Windows to start with a LIMITED set of processors and physical memory. However, contrary to some misconception in an attempt to speed up Windows startup, specifying the maximum number of processors and the entire amount of RAM at the moment of startup will NOT affect the boot speed.

But your system may be configured in such a way that redistributing I/O and IRQ resources along the PCI bus (and this is what this checkbox does) will cause a system failure upon boot, and you will inevitably encounter a startup error: it will be either a black screen or BSOD. If you encounter this problem, try booting into Safe Mode and removing the “check” from the item, or you will have to clear the CMOS memory with a battery or jumper. It's okay - everything can be fixed. In general, when experimenting in this part of msconfig, remember:
By default, Windows devotes all its efforts and resources to launch, and it does this based on the results of the POST check carried out by . At the same time, the system selects the startup and operation parameters for itself EVERY TIME during boot, and it is better not to interfere with this process.
Next option debugging– an even more unknown test tool for mere mortals for developers of drivers for new devices. Work with potential drivers is carried out at the level, and for work it is necessary to use a special control channel. It is highlighted immediately after this option is activated. Debugger/debugger (type WinDbg), connected via the specified port, will allow you to work out the device under study. However, if Windows does not detect it on the default COM1 port (if the settings of the debugger itself are incorrect), the system may very well freeze. Ordinary users who do not use debugging when solving problems or solving problems related to software development for Windows have nothing to do here.
Msconfig: Services Tab
Everything is simple here. The list shows services that start at boot and are running right now. The option Do not display Microsoft services is often useful here if we are interested in third-party programs downloaded with Windows. By checking or unchecking the box, you can check the influence of a particular program on startup if you are going to catch the culprit of unstable operation.

The settings applied here are consistent with the settings in the tab Are common. As soon as you add or remove a service from this list, the startup option in the first tab will change to Selective.
In Windows 10, the contents of the tab moved to the Task Manager, but owners of previous versions could at least somehow control the ever-expanding list of programs that launched along with Windows right from here, slowing down the boot process. Plus, the background hangs in the number of running processes, slowing down work in the current session:

the list of automatically downloaded programs is now here

but autoloading in windows 7 was possible
However, to get the most complete understanding of startup management, it is better to pay attention to the article
Msconfig: Tools Tab
The tab, unlike the previous ones, allows you to run the selected process right now using the button Launch. Moreover, this is done on behalf of the administrator, indicating the full path to the executive file in the system directory. All the utilities listed here are not just anything, but those that belong to the repair or statistical category. Knowing what tools are available from here can be a huge time saver without knowing.
 In addition, it is possible to add the programs we need, similar to existing ones.
In addition, it is possible to add the programs we need, similar to existing ones.
Read: 2,659
Every computer has built-in software. Over time, the operating system experiences minor glitches or freezes. To troubleshoot problems or configure the operation of the software, the user can use a standard utility called “System Configuration”.
The msconfig OS configuration in Windows 7 is a powerful tool with which you can configure the autostart of components and services, as well as eliminate errors that interfere with stable operation. You can open the configurator in various ways.
How to start the system configurator
You can launch “System Configuration” in a fairly simple way. To do this, you need to call the “Run” application. The program is launched using the Win+R key combination. In addition, you can find the application in the general list of standard programs in the Start menu. After starting the program, you need to write msconfig in the line and click the Enter key.

Please remember that you can launch the Windows System Configurator directly from the Start menu. To do this, open the menu and enter the desired msconfig command in the bottom search bar.
The essence of the program
After clicking OK, a new dialog box will appear that allows you to make various system settings. The Windows Configurator has a wide range of settings, which is why the main program window is divided into several tabs. On the first tab of the configurator, you have the right to select a download.
For example, when Windows is running without interruptions, the checkbox is checked for normal boot. However, if there are problems, you must select a diagnostic run and reboot the system. Selective launch is used only when additional launch testing is needed.
The second tab configures OS loading. When several versions of the OS are installed, it is possible to set the startup of the priority system. The Services tab opens a complete list of services that start simultaneously with Windows startup. Experienced users can disable unnecessary services themselves.
On the startup tab, the user can choose to launch applications simultaneously with the system startup. The Service tab contains a large number of different applications with which you can find out about the status of the license and software build version, or restore the OS to an earlier state. 
Running System Customizer on Windows 8
Most users of the modern Windows 8 system are wondering how to enter msconfig windows 8. The procedure for opening the OS Configuration utility is no different from working in 7. You can choose to open the Run program and enter msconfig. Another way to enter the customizer is used on devices that do not have a keyboard and use a touch screen for input. To open, select the search icon on the right side of the desktop. Then you need to enter the name of the msconfig utility to be launched into the search bar. It is worth remembering that it is necessary to indicate the permission of the program. In our example, this is a permission file (.exe).
Complicated ways to run msconfig
Previously, simple ways to launch the configurator were given. However, for some reason the user was unable to launch the settings, then how to enter msconfig windows 7. The user will have to use the Control Panel. Having opened the panel, you should initially change the view by category to large or small icons.
 A new window that opens will allow you to select the “Administration” shortcut. After opening, a new list will appear and the msconfig function will become available for launch.
A new window that opens will allow you to select the “Administration” shortcut. After opening, a new list will appear and the msconfig function will become available for launch.