Complete configuration of the Windows swap file. Swap file
Virtual memory allows you to expand your RAM ( RAM - Random Access Memory), using disk space in this capacity through a technology called paging ( paging). The essence of this technology is that a special file is created on the hard drive called the paging file ( paging file), into which data that is not currently in use is written from RAM. When the data is needed, it is returned to memory, possibly displacing another block of data onto the hard drive.
The initial paging file is created automatically on the hard drive on which the operating system is installed. By default, paging files are not created for other drives, so if necessary, they must be created manually. When a paging file is created, it is given an initial and maximum size. In Windows 8, the page file is called pagefile.sys

In Windows 8.1, the paging file size is set to at least twice the total amount of physical memory installed on the computer. This helps avoid page file fragmentation, which can cause system performance degradation. When manually managing virtual memory, page file fragmentation can be reduced by setting its initial size to be at least equal to the total amount of physical memory.
If the amount of RAM installed is 4 GB or less, the maximum page file size should be at least twice the amount of RAM. If the amount of installed RAM is greater than 4 GB, the maximum size of the paging file should be at least one and a half times the amount of physical memory (or as recommended by the computer manufacturer). This helps maintain file integrity and write data to it in the form of contiguous blocks (if possible given the available volume space).
Setting up virtual memory
To configure virtual memory, follow these steps:
Open dialog box Performance Options, to do this, press the key combination + Q and in the search field of the sidebar that appears Search type systempropertiesperformance and press the key Enter ↵

In the dialog box that opens Performance Options go to the tab Additionally

On the tab Additionally window Performance Options click the button Change...

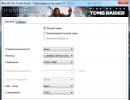
A dialog box will open Virtual memory

This window provides the following information:
Disk [volume label] And Swap file (MB). Information about the current system virtual memory settings. For each volume, its paging file (if any) is indicated. The paging file size range specifies its initial and maximum sizes.Total paging file size on all drives. This section contains information about the recommended amount of virtual memory for the system and the currently allocated amount. Please note that (in most cases) the system disk has already been allocated the recommended amount of paging file, as indicated by the selected switch System selectable size
By default, Windows 8.1 manages the paging file size for all drives. To manually manage virtual memory, clear the checkbox

In the list of drives, select the drive for which you want to configure a paging file.

Set the switch Specify size and enter values for the initial and maximum paging file sizes.

Click the button Set to apply the specified settings.

After completing the settings, click the button OK. If a window appears asking whether to overwrite the old file pagefile.sys new, press the button in it Yes
If you change settings for the paging file that is currently in use, you will be prompted to restart your computer for the changes to take effect. Click the button OK

OK. When closing the window Properties of the system A message appears stating that the computer must be restarted to apply the changes.
Automatic virtual memory management
To configure Windows 8.1 to automatically manage virtual memory, follow these steps:
On the tab Additionally dialog box Performance Options click the button Change to open the dialog box Virtual memory

Check the box in this window Automatically select paging file size

Close all open dialog boxes by clicking the button in them one after the other OK
Good day, dear friends, acquaintances and other personalities. Today we will talk again about what is swap file, what are the correct sizes and why.
In the first part of this series, I wrote about what a paging file is, how to create it, what size it should be and where it should be located (i.e. that article contains a block of information necessary to read this one).
Somehow it so happened that the second part of the article will also touch on the paging file, namely a number of subtleties on its configuration, paging file sizes for different amounts of memory, and all that stuff.
Paging file and size - theory
Empirically, it was possible to prove that large paging file sizes are not good, or rather, often even bad. With large file sizes and busy RAM, the system increasingly turns to the paging file (i.e., the hard drive), and not to the RAM itself, which, firstly, reduces performance (RAM is still faster than the disk).
Secondly, this heavily loads the disk (which also affects performance because the disk is also engaged in other operations with files, and here it also has to tinker with the paging file).
What is enough?
- This is when, when performing any tasks you need, there is always free RAM above 30% and the system does not complain that it does not have enough virtual memory;
- In general, for example, I rarely noticed that 4 GB of RAM (even with a system heavily loaded with processes and games) had little free RAM left, just as with a bunch of running applications in Windows there were some problems on 8 GB. So why load the disk by accessing the paging file and lose performance?
Many, of course, will say that it’s a no-brainer to install so much memory and also leave it free... I don’t know, if performance is more important to you, then the extra 100 rubles should not bother you, since the price of RAM is now simply ridiculous (at at the time of writing, 4GB 1600MHz DDR3 cost less than 1300 rubles), especially since the performance gain is obvious. Anyway, to the point.
Paging file and sizes, practice: which are correct and why
In the course of a year's practice, I derived a series of numbers for each amount of memory so that I could adequately set the paging file, based on the amount of RAM. Here they are.
- 512 Mb 5012-5012 Mb;
- 1024 Mb RAM, - the optimal size of the paging file from 4012-4012 Mb;
- 2048 Mb RAM, - the optimal size of the paging file from 3548-3548 Mb;
- 4096 Mb RAM, - the optimal size of the paging file from 3024-3024 Mb;
- 8 GB RAM, - the optimal size of the paging file from 2016-2016 Mb;
- 16 GB RAM (and more) - most often, without a swap file.
In fact, the more RAM you have, the less you need a paging file and the faster the system will work without it at all (by reducing access to the disk, as well as unloading data there, i.e. everything will be taken directly from memory ).
- Note 1. These dimensions are not extremely accurate and are not recommended for everyone. Rather, this is some kind of average value for the majority, but it all depends on how optimized your system is, what you do on the computer, in what mode, etc., etc., i.e. you can select the paging file specifically for yourself based on your needs and increase/ reduce the value if necessary.
- Note 2. Some applications (games, software, etc) require a swap file, regardless of the amount of memory. In this case, the file should be left even at 16 GB. Even more (by orders of magnitude) than the values mentioned above.
- Note 3. The paging file is needed in larger sizes (different from the above) if you minimize applications and switch to others, leaving the application(s) running (this is important), because minimized applications are often unloaded into this very file. In this case, increase the swap.. Or add memory :)
- Note 4. The recommendations do not apply to server operating systems and relate strictly to user operating systems.
My personal opinion is that if the amount of RAM exceeds 6 GB, the paging file is not needed at all, which gives a noticeable breakthrough in system performance, extending the life of the hard drive and reducing its fragmentation.
Page file and why we choose the same sizes
The swap file, like any other, tends to fragment, which raises the question of the need for defragmentation (read about what defragmentation is and why it is needed) in order to return to its former performance. However, there is a way to reduce the speed and severity of file fragmentation.
To do this, you just need to set the maximum and minimum sizes to be the same:
If you have any questions, I will be happy to answer them in the comments or using .
PS: The last adjustment to the paging file size was made in August 2017, the data was tested on Windows 7, 8 and 10 (x64 bit size).
A paging file is an area allocated on a hard drive (HDD), solid-state drive (SSD) or removable media into which data will be unloaded from RAM under high loads. Simply put, this feature is designed to increase the performance of your computer.
Realizing this, many users are interested in how to increase the paging file on Windows 8. Another popular request is the optimal size for it.
Changing the paging file size
Open the root section of Explorer. In an empty area of the window, right-click, select properties. Find the inscription in the left block "System protection" and click on it.  There is a faster option to access this element: press Win + R at the same time. In the dialog menu, enter sysdm.cpl and run the command. Further actions:
There is a faster option to access this element: press Win + R at the same time. In the dialog menu, enter sysdm.cpl and run the command. Further actions:

Here you can set the size of the paging file, select a disk to host it on, and disable the feature completely. Two setting modes are available: automatic and manual. In the first case, the system itself will determine all the parameters. But customization is also possible, which will be discussed in the next section of the article.
Optimal paging file size
But the opinion of the Microsoft developer is worth listening to. One of the employees of the Sysinternals division, responsible for setting up technical software, said that the optimal volume can be calculated using the following dependence:
- The minimum value is determined by the difference between the actual amount of RAM and the computer's RAM consumption under heavy load.
- And the maximum size is equal to the value from the previous paragraph multiplied by two.
How to increase the performance of Windows 8. Increase RAM using the page file. What is a paging file, why is it needed and how to install it.
RAM is one of the important elements in a computer that is responsible for the speed of performing tasks assigned to it. The more RAM (Random Access Memory) you have, the faster running processes on your computer will run.
In modern computers running Windows 8, it is recommended to install at least 6 GB of RAM, and a minimum of 4 GB. If you have 8 GB or more, then you don’t have to worry about increasing it; this amount can cope with all the tasks of an ordinary user.
But who has 4 GB is better to increase. There are two ways to do this - buy in the store and using a swap file. For those who cannot afford the first method, today I will tell you about the second.
What is a paging file and why is it needed?
This is simply allocated space on your hard drive specifically to help your RAM. When you run several processes at the same time (programs, browser, ISQ, etc.) your memory may not cope.
That's when the page file works, adding RAM space on the hard drive for processing processes.
Of course, such a process requires more time than performing tasks only in the most operational way, but in the absence of it, it will be better than nothing, as they say - for lack of fish, fish for cancer. 🙂
For users who have 8 GB or more and who do not use graphic editors (Photoshop, 3Dmax) and do not play computer video games (where graphics are used), they can completely disable the page file.
Because RAM itself processes user tasks faster without using a page file.
By default, for all operating systems, the paging file is installed on the partition (disk) on which the system itself is located and has a dynamic (changeable) size to be able to allocate space as much as RAM is needed.
Today we will install it on another partition and configure it for your computer.
How to properly install the paging file and configure it
You need to install the paging file on a partition where you do not have the system itself and the most free space. Usually the system is installed on the partition with the letter “C”, and other partitions can have letters starting with “D”.
Also, after installing on the “D” partition, make sure that you have disabled the paging file on other partitions, so as not to create additional load on the disk.
Do not install a paging file if you have less than 10% free disk space left after you add paging, this will lead to increased disk load, which is not even more desirable than low RAM.
There are two versions of setting up the paging file:
- static - of a certain size,
- dynamic - resizable.
In the first case, we ourselves set the amount of space that the RAM can request. Accordingly, we set the minimum and maximum numbers equal to your RAM.
It is believed that in this case the paging file is not subject to fragmentation (empty spaces on the disk) and works better.
The second case suggests making dynamic paging, when the minimum volume is equal to the amount of your RAM, and the maximum is its double value.
I recommend using the second option, because... I find it more productive. And you can fight fragmentation by configuring it to be cleaned after completion of work.
So let's move on directly to the steps to configure the paging file.
Open the right tab and select “Options”

Go to “Computer Information”

We look at the amount of installed RAM (RAM)

Open “Advanced system settings”, a small new “System Properties” window will open. In the “Performance” section, click “Options”

In the new “Performance Options” window that opens, go to the “Advanced” tab and in the “Virtual Memory” item, click the “Change” button

- We select a disk with more space or simply not the one on which the system is installed
- Check the box next to “Specify size”
- We write down our values
- Click the “Set” button
- And click “OK”

- Next, select the disk (or disks in turn), where it says “By system choice”
- Check the box next to “No paging file”
- Click the “Set” button
- If a window pops up, click “Yes”
- And click “OK”

To do this, select the “Run” command in the “Start” menu; if it is not there, then look in “All applications”

In the window that opens, write secpol.msc and click “Ok”


- Click "Properties"
- Select “Enabled”
- "Apply"
- And "OK"

Afterwards you will need to reboot. You can do it right away or later.

Now you know how to increase the performance of Windows 8 without buying anything. 🙂
P.S. Write in the comments whether you use a swap file or maybe you have other methods?